Investment Casting vs Die Casting: Which Is Suitable for Your Application
Casting is a well-established manufacturing technique that has been used since the 1890s. Two commonly used casting technologies today are investment casting and die casting. While these techniques share the same basic principles, there are specific differences between investment casting and die casting. Investment casting involves the injection of wax into an aluminum cavity, whereas die casting forces molten metal into mold cavities at high pressure.
This article provides an overview of these techniques and highlights their key benefits. By understanding the differences between investment casting and die casting, you can make an informed decision about the best option for your project.
What Is Investment Casting?
The investment casting process revolves around the lost wax casting principle. It entails coating a wax mold by dipping it into a slurry of refractory material, resulting in the mold becoming "invested" within the refractory material.
Once the final coating hardens, the wax is melted off through heat, leaving behind a mold cavity in the shape of the component. Molten metal is then poured into the cavity, replacing the wax pattern with metal. The metal cools and solidifies within the mold before the cast part is removed.
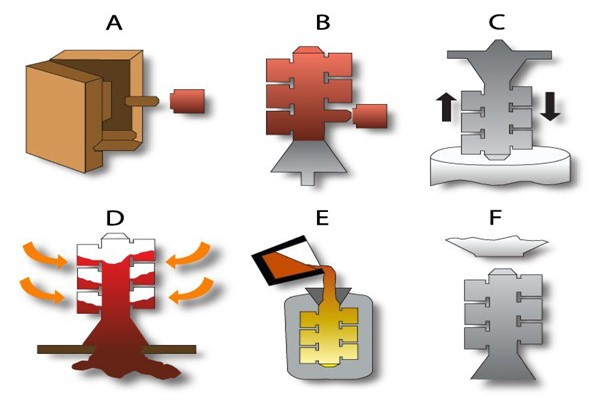
Key Advantages of Investment Casting: Here are the various benefits of using investment casting for your project:
Flexible Design: Investment casting allows for freedom of design, making it ideal for complex parts. It is compatible with various materials, including aluminum alloys, cast iron, and non-ferrous metal alloys. Additionally, this casting technique is highly adaptable and does not have limitations in terms of size, shape, or thickness.
Tighter Tolerances and Intricate Shapes: Investment casting is a precision casting method that provides consistent tight tolerances and intricate shapes. Typical tolerances for investment casts range between +/-0.010" and +/-0.004". Unlike similar processes, investment casting enables the production of near net shape and net shape components, reducing the need for further post-processing and associated costs.
Superior Surface Finish: The wax patterns used in investment casting come with a standard 125 micro finish. This results in components with accurate and smooth surfaces that outperform other casting processes. Investment castings do not have parting lines since only one mold is involved in their processing. In some cases, finishing operations may not be required.
Customizable Size Range: Depending on your project's requirements, investment casting can produce both small and large casts. Manufacturers can cast parts ranging from as small as 0.1kg up to 100kg. Furthermore, investment casting does not require large quantity demands before production and can produce as few as 10 pieces while still saving costs.
What Is Die Casting?
The die casting process involves melting non-ferrous alloys and injecting them into pre-existing molds within die casting machines. There are two main industrially used die casting
Processes:
Hot Chamber Die Casting: This process involves melting metals and injecting them into dies at high pressure using a hydraulic system. It is suitable for low melting point metals such as zinc, magnesium, lead, and tin alloys.
Cold Chamber Die Casting: In contrast to the hot chamber process, cold chamber die casting ladles the molten metal into a cold chamber before injecting it into the die. The pressure in this process is usually between 2000 and 20000 psi, and it is suitable for high melting point metals like aluminum.
Once the molten metal is injected, it rapidly cools and solidifies to form the final casting. Castings produced through die casting can vary in size and weight, making them suitable for various applications.
Key Advantages of Die Casting:While there are several pros and cons to die casting, the following are the major benefits of the process:

High Mechanical Properties: Castings created through die casting exhibit excellent mechanical properties. As the molten metal solidifies under pressure, the resulting product appears compact, fine, and crystalline. These components are rigid, offering high strength, hardness, conductivity, and durability.
High Dimensional Accuracy: Die casting produces components that maintain their dimensional accuracy over a long period. They also maintain tighter tolerances with minimal variations. As a result, this process is suitable for fabricating complex machine parts that require high precision standards, eliminating the need for further machining.
Creates Complex, Thin-Walled Parts: Aluminum die casting, in particular, enables the production of lightweight and complex components with excellent strength-to-weight ratios. This advantage sets it apart from many other metal casting methods. Die casting can create aluminum parts with a thickness of about 0.5mm, and zinc parts can have a wall thickness as low as 0.3mm.
Smooth Surface Finishes: Die-cast components have consistently smooth and crystalline surfaces. Well-shaped dies and proper conditions result in smooth and fine parts, often requiring minimal additional post-processing operations. This helps reduce the total cycle time for production.
Investment casting and die casting offer distinct advantages depending on your project's requirements. Investment casting provides design flexibility, tighter tolerances, intricate shapes, superior surface finish, and a customizable size range. On the other hand, die casting offers high mechanical properties, dimensional accuracy, the ability to create complex thin-walled parts, and smooth surface finishes. Consider the specific characteristics and needs of your application to determine the most suitable casting method.
A Detailed Comparison: Investment Casting Vs Die Casting
Now that you understand the two processes and their key advantages, it’s time to compare investment casting vs die casting. The table below succinctly summarizes their differences to give you a clearer view.
Investment Casting | Die Casting | |
Working Process | Forms molds with liquid ceramic slurry | Forces molten metal into the die cavity at high pressure |
Casting Material Selection | Ferrous and non-ferrous metals | Non-ferrous metals |
Design Complexity | High design flexibility | Considerable flexibility |
Part Size | Small to medium-sized parts | Larger parts |
Surface Treatment | Best surface finish | Good surface finish |
Production Volume | Less than 10,000 pcs | Over 10,000 pcs |
Tolerance | +/-0.005 inches | Standard:+/-0.010 inch |
Cycle Time | Hours of casting | Up to 100 shots per minute |
Applications | Aerospace, firearm, military, automotive, energy, commercial, and beverage industries | Consumer, industrial, and commercial products |
Let’s go into a more detailed comparison based on the following sections:
Working Process:
The investment casting process begins with the creation of a wax pattern, which is used to produce the desired end product. The operator attaches the waxes to sprue bottoms and repeatedly dips them into a ceramic mold. Once the ceramic hardens and takes the shape of the casting, the mold is heated to melt the wax. Molten metal is then poured into the mold cavity, and after the metal cools and solidifies, the mold is broken to remove the cast part.
On the other hand, die casting involves the injection of liquid metal into a cavity at high pressure. Technicians use a hardened steel tool to create die cavity trees that have the shape of the required products. Molten metal is placed on a sleeve and forced into the die cavity using a piston, applying continuous pressure as the metal fills the die. Once the metal cools, the operator removes the tree and extracts the component. Typically, the part will require secondary machining for a complete finish.
Casting Material Selection:
Investment casting is suitable for a wide range of metal alloys and works well with both ferrous and non-ferrous metals. This casting process can accommodate materials such as stainless steel, copper, aluminum, zinc, and more. It also enables the casting of alloys that may be challenging to machine.
On the other hand, die casting is ideal for non-ferrous metals, including aluminum, zinc, copper, lead, and magnesium alloys. Therefore, investment casting offers a broader range of material options compared to die casting.
Design Complexity:
When comparing investment casting to die casting, design geometry plays a crucial role. Investment casting can achieve more precise dimensions, thin-walled components, and other complex geometries. This technique provides greater design flexibility, allowing for the incorporation of various design features and the casting of intricate parts.

While die casting can produce larger components and yield good dimensional results, it cannot offer the same level of intricacy as investment casting.
Part Size
Investment casting accommodates components from 0.02 kg up to about 100 kg. However, there are some limitations to the size of the parts for this process. This is because of the need to securely gate the wax pattern to the tool sprue to ensure repeated dipping in the refractory material slurry.
On the other hand, die casting can produce much larger components with fewer size limitations. You can basically get any past size with this process. However, creating large parts with die casting will require larger tooling and unit costs.
Surface Treatment
When you compare die cast vs investment cast, you will see that the surface finish on an investment cast is better than with a die-cast component. The standard precise tolerance for this process is IT5-6, and you can get up to 125 micro finishes. This reduces or eliminates the need for secondary machining.

Die casting surface finishes are also good enough. However, parts made with this process will require additional machining to reach desired results.
Production Volume
Investment casting is much more suitable for low-volume production runs, usually less than 10,000 pcs. In contrast, die casting is ideal for high-volume projects and larger production runs of over 10,000 pcs because it can produce between 100 to 2000 parts per hour. Although the mold cost may be high, one mold can produce up to one million components. Moreover, the process ensures excellent repeatability and consistency, making it ideal for large runs.
Tolerance
Both investment and die casting can produce good and tight tolerances. However, the tolerance capabilities of a casting process depend greatly on the kind of material used and the part’s shape.
The general rule is that smaller parts have greater dimensional accuracy. Therefore, investment casting delivers more on tight tolerances (about +/-0.005 inches) when it comes to smaller components. However, large investment castings usually lose some of their dimensional accuracies. In such cases, die casting will be the better option for large pieces because it can offer standard tolerances of +/-0.010 inch and precision tolerance of up to +/-0.002 inch.
Cycle Time
Conventional investment casting is quite time-consuming, requiring some labor and hours of casting. On the other hand, traditional die casting can produce up to 3 to 4 shots per minute. Multi-side die casting can create over 45 shots per minute or even up to 100 shots per minute for smaller components. Die castings are often produced with complete automation, involving little to no human involvement.
Investment Casting vs Die Casting: Which Is More Cost-Effective?
Production volume plays an important role when comparing the cost of production for investment casting vs die casting. If you’re working with a large production volume of over 10,000 pieces, then die casting will be more cost-effective than investment casting. Since there’s more automation with die casting, manufacturers can produce more parts within a short period.
On the other hand, investment casting is much more cost-effective for small volume production runs of less than 10,000 pcs. Die casting machines are more expensive, and low-volume runs cannot compensate for the die casting cost. Investment casting requires lesser machinery, thereby saving tooling costs. Moreso, investment castings often don’t need secondary machining. As a result, you can further save machining costs.
If you’re having difficulty deciding the best technique for your project, you need to seek professional help. Dongruncasting is ready to offer you the best and most reliable investment casting and die casting services. Our experienced technicians are well-versed in these casting technologies and will provide expert advice to help you get the best from your project.
Our online quotation platform also provides instant quotation when you upload your design files, with DFM analysis reports to optimize your design for cost reduction. Upload your CAD file today, and let’s get started!
Conclusion: Die Casting vs Investment Casting, Which Suits Your Needs Better?
While die casting and investment casting are well-established techniques, they are best suited for different applications. Your choice of casting method will depend on your specific needs. For instance, die casting is best for creating a large batch of parts quickly, cost-effectively, and with good consistency. On the other hand, investment casting is preferred for smaller products with complex or intricate features.
Die casting is also suitable for only non-ferrous metals like aluminum, zinc, copper, etc. However, investment casting will be your best choice if you need to make a part from ferrous metals like stainless steel. Generally, your manufacturing requirements will determine the best process to choose.
ZheJiang Dongrun Casting Industry Co,.Ltd was built in 1995, We have been in the casting industry for more than 25 years. No matter what type of molding you need done, we are the right supplier for your jobs. Unlike other of our competition, we offer four types of castings.

Dongrun Casting have 20000 square meters facility houses and 200 production & test equipment, From quotation and tooling design to casting and finished machining, we can work with you at every stage. We serves wide range of industries-from Fortune 500 corporations to small and midsize OEMs. Our products includes:
❖ HVAC | ❖ Architectural parts |
Browse our online showroom to see what we can do for you. And then E-mail:dongrun@dongruncasting.com us your specifications or inquiries today
