Low Pressure Die Casting: A Comprehensive Guide to the Process
Low-pressure die casting is an advanced manufacturing technique that involves injecting molten material into a die-cast under precisely controlled low pressure conditions, offering numerous advantages. The automotive industry, in particular, benefits from this process, producing accurately manufactured axially symmetrical components like wheels. Before considering outsourcing to a die casting service, it's essential to understand this process. This article provides a detailed introduction to low-pressure die casting, its workings, advantages, disadvantages, and alternative methods.
What is Low-Pressure Die Casting?
Low-pressure die casting (LPDC) involves filling a die-cast mold with molten metal under low pressure conditions. Its accuracy is a result of maintaining low pressure during solidification, which ensures continuous filling of the die cavity, compensating for volume reduction. LPDC minimizes oxide formation, porosity, and offers consistent molten metal quality from top to bottom.
How Does Low-Pressure Die Casting Work?
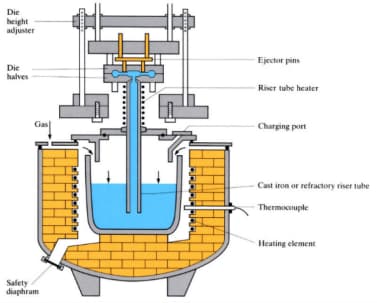
Low-pressure die casting employs modest pressure, typically around 20-100 kPa (2.9-14.5 psi), instead of gravity to fill a die. It involves a specialized setup and various equipment pieces. The process follows these key steps:
Melting Furnace: The process starts with a melting furnace, which heats metal alloys to their casting temperature, such as 710-720°C for aluminum.
Holding Furnace: Below the mold, a holding furnace maintains the molten metal at the casting temperature, serving as a reservoir.
Molten Metal Injection: Low pressure forces the molten metal through a riser tube into the mold. The molten metal continues to flow under constant pressure until it solidifies within the die cavity.
Pressure Release: After solidification, the pressure is released, and any remaining molten metal returns through the riser tube to the holding furnace for recycling.
Casting Removal: Once the mold cools, the casting is easily removed.
Advantages of Low-Pressure Die Casting
Low-pressure die casting offers several advantages, making it a valuable method in various industries:
High Accuracy: Parts produced via this process are exceptionally accurate due to continuous low-pressure filling, compensating for volume shrinkage during solidification. It is the preferred method for crafting axially symmetrical components such as wheels.
High Purity Castings: Low-pressure castings are exceptionally pure due to minimal slag impurities. The setup prevents the inclusion of slag in the liquid metal, ensuring high casting purity.
Good Formability: The low-pressure filling process improves the fluidity of liquid metal, resulting in clear outlines and smooth surfaces. This makes it ideal for crafting parts with complex geometries.
Crystallization: The casting solidifies under pressure, allowing for the formation of a compact, dense structure. As a result, castings have excellent strength properties, suitable for parts requiring high strength.
Disadvantages of Low-Pressure Die Casting
Despite its advantages, low-pressure die casting has some limitations:
Slower Casting Cycle: The low-pressure process has a slower cycle due to its low-pressure nature, resulting in a lower production volume and higher part cost.
Metal Erosion: Contact between the molten metal and equipment parts can lead to erosion of those parts, increasing maintenance costs, particularly in larger setups.
Not Suitable for Thin-Walled Parts: This process is not ideal for creating thin-walled components; the minimum wall thickness achievable is around 3mm.
Low-Pressure Die Casting vs. High-Pressure Die Casting
Low-pressure and high-pressure die casting are suitable for different applications, depending on component complexity, production volume, and budget. Key differences between the two methods include:
Cycle Time: Low-pressure die casting has a shorter cycle time due to its lower pressure range, typically 0.7 to 1 bar, whereas high-pressure die casting operates at significantly higher pressures (often over 1000 bars).
Strength of Parts: Low-pressure castings are known for their high strength properties due to the slow solidification process. High-pressure castings also have good strength, but they cannot match the strength of low-pressure castings.
Casting Quality: Low-pressure castings have superior quality, featuring minimal impurities and no pores. This contrasts with high-pressure castings, which can contain pores and impurities due to the higher pressures involved.
Cost: High-pressure die casting requires more substantial initial investments in machines but has lower part costs due to shorter cycle times. Low-pressure die casting has lower operating costs but higher part costs.
Thickness: Low-pressure casting is ideal for thick parts, while high-pressure casting is suitable for thin-walled components.
Alternatives to Low-Pressure Die Casting
Although low-pressure die casting is highly effective, specific conditions may necessitate alternative methods, including:
Gravity Casting: Gravity die casting, also known as permanent mold casting, relies on gravity to fill the mold with molten metal. It is suitable for a wide range of non-ferrous alloys such as aluminum, copper, magnesium, and zinc.
Investment Casting: Investment casting, or precision casting, employs wax patterns for precise mold creation. It is highly accurate and is ideal for complex geometries.
Sand Casting: Sand casting, a traditional method used in foundries, is suitable for high-heat metals and offers a wide range of material compatibility.
In conclusion, low-pressure die casting is a precise and efficient manufacturing process, particularly suited for complex, high-strength components. While it has a slower cycle time and certain limitations, it remains a valuable method for numerous industries. Understanding the process, its advantages, and potential alternatives is crucial for informed decision-making in manufacturing projects.
Dongrun Casting have 20000 square meters facility houses and 200 production & test equipment, From quotation and tooling design to casting and finished machining, we can work with you at every stage. We serves wide range of industries-from Fortune 500 corporations to small and midsize OEMs. Our products includes: Automotive&Trucking, Electric Utility & Communications, Metering System, Hydraulic Industry, Medical Devices, Lighting, Fuel and Gas Pressure, Furniture parts.
More Details : www.dongruncasting.com
